Implementing iPad Cross-Hierarchy Auto Layout Constraints in iOS 6
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
| Implementing iPad iOS 6 Auto Layout Constraints in Code | Understanding the iPad iOS 6 Auto Layout Visual Format Language |
Learn SwiftUI and take your iOS Development to the Next Level |
One of the few types of auto layout constraint that cannot be implemented within the Interface Builder environment is one that references views contained in different view hierarchies. Constraints of this type must, therefore, be implemented in code. Fortunately, however, the steps to achieve this are quite simple. The objective of this chapter is to work through an example that demonstrates the creation of a cross-view hierarchy auto layout constraint.
The Example Application
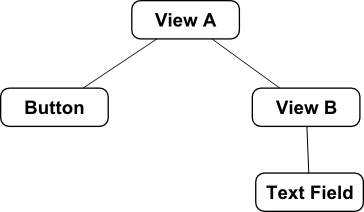
For the purposes of this example, a very simple user interface will be created consisting of two Views, a Button and a Text Field. In terms of the physical view hierarchy, the user interface will be constructed as outlined in Figure 21-1.
Figure 21-1
The goal will be to implement a constraint that aligns the centers of the Button and Text Field which are part of different view hierarchies - the button being part of the hierarchy contained by View A and the text field being part of the View B sub-hierarchy.
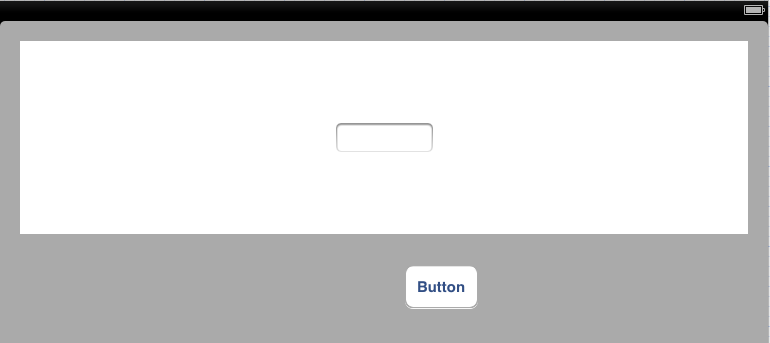
In terms of visual layout, the user interface should appear as illustrated in Figure 21 2. Key points to note are that the text field should have constraints associated with it which horizontally and vertically center it within View B and the button view should be positioned so that it is slightly off center in the horizontal axis:
Figure 21-2
Begin by launching Xcode and selecting the options to create a new iPad iOS application based on the Single View Application template. Enter CrossView as the product name and class prefix, set the device to iPad and select the Use Storyboards and Use Automatic Reference Counting options if they are not already selected.
Select the MainStoryboard.storyboard file from the project navigator panel and drag and drop UIView, Button and Text Field views onto the design canvas as illustrated in Figure 21-2, making sure to center the text field object horizontally and vertically within the parent view.
Establishing Outlets
Ctrl-click on the Text Field object in the view and drag the resulting line to the area immediately beneath the @interface directive in the Assistant Editor panel. Upon releasing the line, the configuration panel will appear. Configure the connection as an Outlet named myTextView and click on the Connect button. Repeat the above steps to add an outlet for the button object named myButton.
As currently constrained, the text field object is centered horizontally and vertically within the view we are referring to as View B. In place of this constraint, we need the text field to be aligned with the center of the button object. This will involve removing the CenterX constraint and replacing it with a new constraint referencing the button. This requires outlets for both the View B instance and the CenterX constraint.
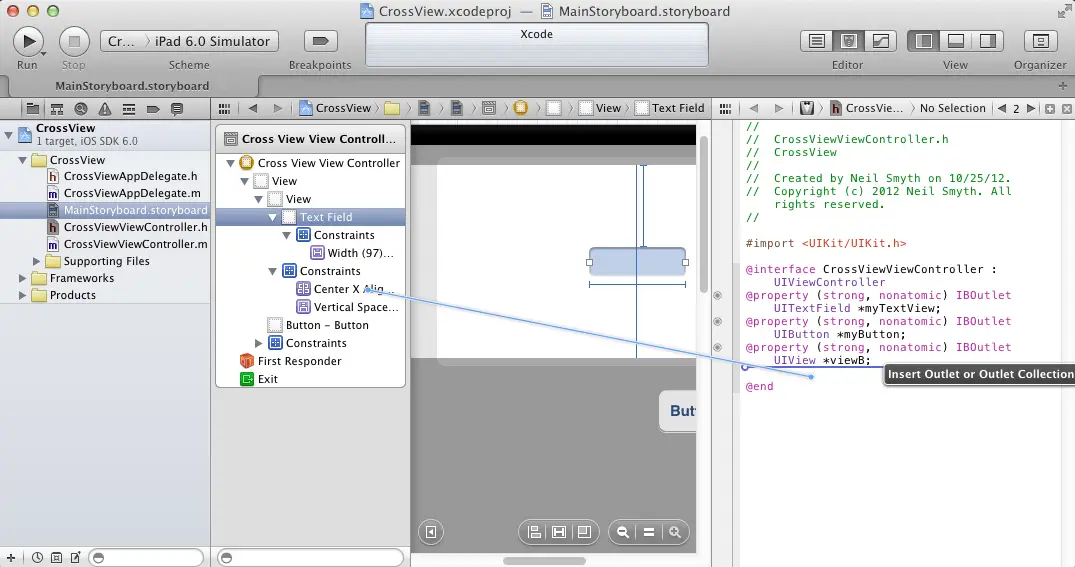
Ctrl-click on the View B parent of the text field object and drag the resulting line to the area immediately beneath the @interface directive in the Assistant Editor. Release the line and configure an outlet named viewB. Next, with the text field selected, locate the CenterX Alignment constraint in the Document Outline panel (Figure 21-3) and create a new outlet for this object named centerConstraint.
Figure 21-3
Writing the Code to Remove the Old Constraint
With the necessary outlets created, the next step is to write some code to remove the center constraint from the text field object. For the purposes of this example, all code will be added to the viewDidLoad: method of the view controller. Select the CrossViewViewController.m file and locate and modify the method as follows:
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
[_viewB removeConstraint:_centerConstraint];
}
All that the code is doing is calling the removeConstaint: method of view B using the previously configured outlet, and passing through a reference to the CenterX constraint, once again using the previously configured outlet to that object.
Adding the Cross Hierarchy Constraint
All that remains is to add the constraint to align the centers of the text field and button. With the appropriate outlets already configured, this is simply a question of creating the NSLayoutConstraint object with the appropriate values, and adding it to the closest common ancestor:
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
[self.viewB removeConstraint:self.centerConstraint];
NSLayoutConstraint *constraint = [NSLayoutConstraint
constraintWithItem:_myTextView
attribute: NSLayoutAttributeCenterX
relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
toItem:_myButton
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeCenterX
multiplier:1.0
constant:0.0];
[self.view addConstraint:constraint];
}
Testing the Application
Compile and run the application either on a physical iPad device, or using the iOS Simulator. When the application is running, the text field should be aligned with the button and this alignment should be maintained when the device is rotated into landscape orientation.
Summary
The current version of Interface Builder does not provide a way to select two views that reside in different view-hierarchies and configure a constraint between them. The desired result can, as outlined in this chapter, be achieved in code. Of key importance in this process is that fact that constraints, just like any other view object in a user interface, may be connected to an outlet and accessed via code.
Learn SwiftUI and take your iOS Development to the Next Level |
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
| Implementing iPad iOS 6 Auto Layout Constraints in Code | Understanding the iPad iOS 6 Auto Layout Visual Format Language |