Adding a New Disk Drive to a Fedora Linux System
One of the first problems encountered by users these days is that they run out of disk space to store data. Fortunately disk space is now one of the cheapest IT commodities. In the next two chapters we will look at the steps necessary to configure Fedora Linux to use the space provided via the installation of a new internal disk drive.
Mounted Filesystems or Logical Volumes
There are two ways to configure a new disk drive into a Fedora Linux system. One very simple method is to create one or more Linux partitions on the new drive, create Linux filesystems on those partitions and then mount them at specific mount points so that they can be accessed. This approach will be covered in this chapter of Fedora Linux Essentials.
Another approach is to add the new space to an existing volume group or create a new volume group. When Fedora is installed a volume group is created and called VolGroup00. Within this volume group is a logical volume called LogVol00 which is used to store the / filesystem. By configuring the new disk as part of a volume group (for example VolGroup00) we are able to increase the disk space available to the logical volumes. Using this approach we able, therefore, to increase the size of the / filesystem by allocating some or all of the space on the new disk to LogVol00. This topic will be discussed in detail in the chapter entitled (Adding a New Disk to a Fedora Volume Group and Logical Volume).
Getting Started
This tutorial assumes that the new physical hard drive has been installed on the system and is visible to the operating system. The best way to do this is to enter the system BIOS during the boot process and ensuring that the BIOS sees the disk drive. Sometimes the BIOS will provide a menu option to scan for new drives. IF the BIOS does not see the disk drive double check the connectors and jumper settings (if any) on the drive.
Finding the New Hard Drive in Fedora
Assuming the drive is visible to the BIOS it should automatically be detected by the operating system. Typically, the disk drives in a system are assigned device names beginning hd or 'sd followed by a letter to indicate the device number. For example, the first device might be /dev/sda, the second /dev/sdb and so on.
The following is output from a system with only one physical disk drive:
ls /dev/sd* /dev/sda /dev/sda1 /dev/sda2
This shows that the disk drive represented by /dev/sda is itself divided into 2 partitions, represented by /dev/sda1 and /dev/sda2.
Another option is to install and run the Hardware Browser. If this is already installed it may be launched by selecting Hardware from the Application->System Tools->Hardware menu option. If this option is not available it may be installed as follows:
su - yum install hwbrowser
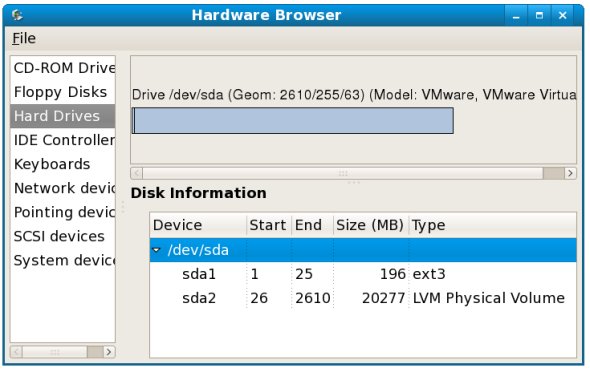
In the Hardware browser select the Hard Drives option to display the current hard disk drive configuration:
The following output is from the same system after a second hard disk drive has been installed:
ls /dev/sd* /dev/sda /dev/sda1 /dev/sda2 /dev/sdb
As shown above, the new hard drive has been assigned to the device file /dev/sdb. At this point the drive has no partitions shown (because we have yet to create any).
At this point we have a choice of creating partitions and filesystems on the new drive and mounting them for access or adding the disk as a physical volume as part of a volume group. To perform the former continue with this chapter, otherwise read hello for details on configuring Logical Volumes.
Creating Linux Partitions
The next step is to create one or more Linux partitions on the new disk drive. This is achieved using the fdisk utility which takes as a command-line argument the device to be partitioned:
fdisk /dev/sdb Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x408bf4fd. Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable. The number of cylinders for this disk is set to 1044. There is nothing wrong with that, but this is larger than 1024, and could in certain setups cause problems with: 1) software that runs at boot time (e.g., old versions of LILO) 2) booting and partitioning software from other OSs (e.g., DOS FDISK, OS/2 FDISK) Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite) Command (m for help):
In order to view the current partitions on the disk enter the p command:
Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 4294 MB, 4294967296 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 522 cylinders Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Disk identifier: 0x338f9c36 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
As we can see from the above fdisk output the disk currently has no partitions because it is a previously unused disk. The next step is to create a new partition on the disk, a task which is performed by entering n (for new partition) and p (for primary partition):
Command (m for help): n Command action e extended p primary partition (1-4) p Partition number (1-4):
In this example we only plan to create one partition which will be partition 1. Next we need to specify where the partition will begin and end. Since this is the first partition we need it to start at cylinder 1 and since we want to use the entire disk we specify the last cylinder as the end. Note that if you wish to create multiple partitions you can specify the size of each partition by cylinders, bytes, kilobytes or megabytes.
Partition number (1-4): 1 First cylinder (1-522, default 1): Using default value 1 Last cylinder or +size or +sizeM or +sizeK (1-522, default 522): Using default value 522
Now that we have specified the partition we need to write it to the disk using the w command:
Command (m for help): w The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Syncing disks.
If we now look at the devices again we will see that the new partition is visible as /dev/sdb1:
ls /dev/sd* /dev/sda /dev/sda1 /dev/sda2 /dev/sdb /dev/sdb1
The new partition will similarly be visible in the Hardware Browser. The next step is to create a filesystem on our new partition.
Creating a Filesystem on a Fedora Disk Partition
We now have a new disk installed, it is visible to Fedora and we have configured a Linux partition on the disk. The next step is to create a Linux filesystem on the partition so that the operating can use it to store files and data. The easiest way to create a filesystem on a partition is to use the mkfs.ext3 utility which takes as arguments the label and the partition device:
/sbin/mkfs.ext3 -L /photos /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.40.4 (31-Dec-2007)
Filesystem label=/photos
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
524288 inodes, 1048233 blocks
52411 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=1073741824
32 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
16384 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (16384 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 38 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
Mounting a Filesystem
Now that we have created a new filesystem on the Linux partition of our new disk drive we need to mount it so that it is accessible. In order to do this we need to create a mount point. A mount point is simply a directory into which the filesystem will be mounted. For the purposes of this example we will create a /photos directory to match our filesystem label (although it is not necessary that these values match):
mkdir /photos
The filesystem may then be manually mounted using the mount command:
mount /dev/sdb1 /photos
Running the mount command with no arguments shows us all currently mounted filesystems (including our new filesystem):
mount /dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00 on / type ext3 (rw) proc on /proc type proc (rw) sysfs on /sys type sysfs (rw) devpts on /dev/pts type devpts (rw,gid=5,mode=620) /dev/sda1 on /boot type ext3 (rw) tmpfs on /dev/shm type tmpfs (rw) none on /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc type binfmt_misc (rw) sunrpc on /var/lib/nfs/rpc_pipefs type rpc_pipefs (rw) nfsd on /proc/fs/nfsd type nfsd (rw) /dev/sdb1 on /photos type ext3 (rw)