Repairing and Defragmenting Windows Server 2008 Disks
The objective of this chapter of Windows Server 2008 Essentials is to cover the subject of checking, repairing and defragmenting FAT, FAT32 and NTFS file systems under Windows Server 2008 using both graphical and command-line tools.
Using Check Disk to Scan For and Fix File System Errors
The Check Disk tool can be used either to scan for and report errors on a file system, or to locate and fix errors. The graphical from of Check Disk can be invoked either from within Windows Explorer or the Disk Management tool. In either case, invoke the tool by right clicking on the drive in question, selecting Properties, clicking the Tools tab and pressing the Check Now... button.
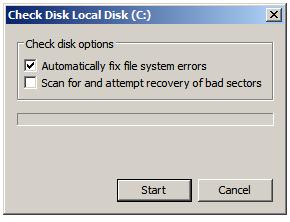
Once invoked, the initial Check Disk dialog will appear providing two options as illustrated below:
If neither of the options are selected when the Start button is pressed Check Disk will only report, but not attempt to fix errors. In order for Check Disk to repair errors and recover bad sectors during the scan the Automatically fix file system errors and Scan for and attempt recovery of bad sectors toggles must be selected respectively.
If the disk drive contains open files, Check Disk will be unable to fix errors located during the scan and will display a dialog warning you of this fact. This warning dialog will also provide the option to have the check run on the next system reboot (before any files are opened). This marks the disk as dirty forcing Check Disk execution at system startup. This setting may also be specified from the command prompt as follows:
fsutil dirty set e: Volume - e: is now marked dirty
The current setting for a volume may be checked at any time using fsutil dirty query:
fsutil dirty query Volume - e: is Dirty
Running Check Disk from the Command-prompt
The Check Disk process my also be initiated from the command prompt using the chkdsk' command combined with the designator of the drive on which the scan is to be performed. In addition to performing the same functions as the graphical version of Check Disk, the command prompt version also provides more detailed disk analysis and repair reports.
The chkdsk utility accepts a number of command line options which govern the tasks performed during execution. These options are outlined in the following table:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| /F | Analyze the disk and fix any errors detected. |
| /B | Reevaluate clusters marked as bad on the volume. |
| /C | Do not check for cycles (a situation where a directory points to itself) within the folder structure. NTFS only. |
| /I | Perform a minimum check of indexes. NTFS only |
| /L[:Size] | Change the size of the transaction log file efault size is m default of 4096 KB. NTFS only. |
| /R | Analyze the disk and fix any errors, chack for bad sectors and mark them as bad. |
| /V | List the full path of every file on the volume on FAT/FAT32. Displays messages related to fixing errors on NTFS volumes. |
| /X | Force the volume to dismount if currently mounted. |