Creating New Databases and Tables with MySQL Administrator
Unless a database already exists, very little can be done with MySQL until a database with at least one table has been created. Databases and tables can either be created using SQL commands (typically using the mysql tool) or using a grpahical administration tool such as MySQL Administrator. In this chapter we will cover the creation of databases and tables using MySQL Administrator. If you prefer to use SQL commands to perform these tasks refer to Creating Databases and Tables Using SQL Commands.
This chapter assumes you have an understanding of databases, tables and columns and have the MySQL Administrator installed, running and connected to a database server (see The MySQL Administrator Tool for details).
Creating a New Database
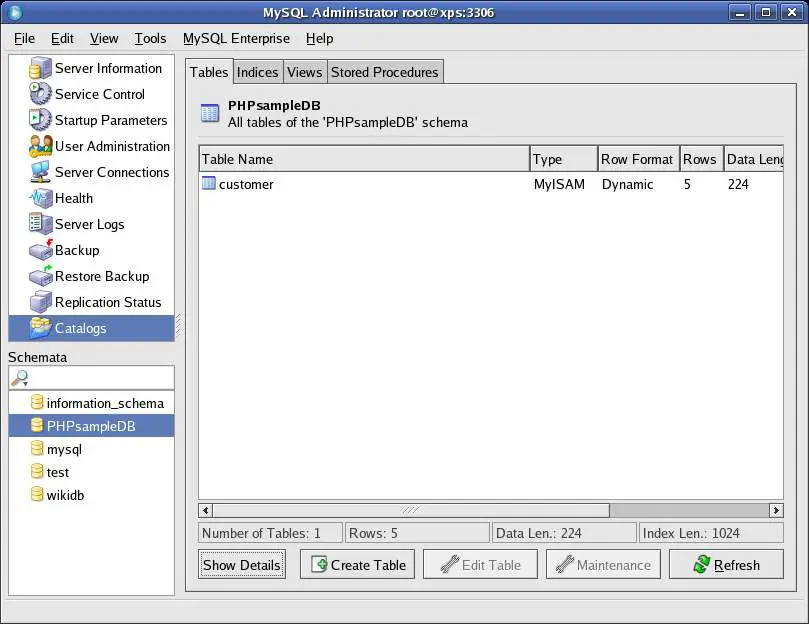
Once MySQL Administrator is running and connected to a database server, the first task is to create a new database. Begin by clicking on the Catalog option on the left hand side of the MySQL Administrator main window. The Catalog screen will then appear as follows:
The area in the bottom left hand corner of the screen entitled Schemata lists the databases currently under the control of the database server to which the administration client is currently connected. Selecting any existing entry in this list will list the tables contained within that database. In the above figure, a pre-existing database named PHPsampleDB is selected, which is shown to contain a single table named customer which contains 5 columns.
The columns in the table may be viewed and modified by selecting the desired table in the list and clicking the Edit Table button.