Difference between revisions of "Configuring Windows Server 2008 NAP DHCP Enforcement"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
The subject of Network Access Protection is large, and as such, much of the detail is beyond the scope of this chapter. In fact entire books could, and probably will, be written on the subject. The objective of this chapter, therefore, is to focus solely on the integration of NAP into DHCP. | The subject of Network Access Protection is large, and as such, much of the detail is beyond the scope of this chapter. In fact entire books could, and probably will, be written on the subject. The objective of this chapter, therefore, is to focus solely on the integration of NAP into DHCP. | ||
| − | NAP Enforcement for DHCP | + | NAP Enforcement for DHCP involves a number of different |
== Installing the Network Policy Server == | == Installing the Network Policy Server == | ||
Revision as of 14:00, 9 September 2008
Network Access Protection (NAP) is a system designed to protect networks from clients which are not deemed to be secure or healthy (to use Microsoft's terminology). When NAP is implemented, clients without the required level of "health", the user is directed to a remediation server where the necessary updates may be obtained to bring the system into compliance with the Network Access policy of the network. In addition, the user may also be directed to a web page provided details of why access to the network has been declined and outlining the steps necessary to remedy the problem.
One way to implement NAP is to integrate it with DHCP so that the NAP policies can be enforced whenever a client attempts to lease or renew an IP address. One point to note before implementing such a configuration is that NAP enforcement will only take place for clients which obtain an IP address via DHCP. Clients with static IP addresses will not be subject to NAP enforcement.
The subject of Network Access Protection is large, and as such, much of the detail is beyond the scope of this chapter. In fact entire books could, and probably will, be written on the subject. The objective of this chapter, therefore, is to focus solely on the integration of NAP into DHCP.
NAP Enforcement for DHCP involves a number of different
Installing the Network Policy Server
The first step in integrating DHCP and NAP is to install the Network Policy Server role on the system. This is achieved by starting the Server Manager, selecting Roles from the left hand pane and clicking on Add Roles. In the Add Roles wizard select the chck box next to Network Policy and Access Services and then click Install to continue the installation process.
Configuring NAP in the NAP console
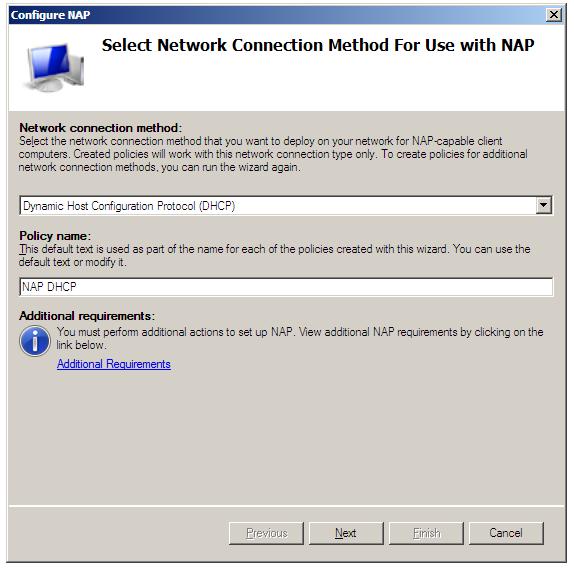
With the Network Policy Server role installed the next step is to configure NAP. Begin by launching the Network Policy console (Start -> All Programs -> Administration Tools -> Network Policy Server). Once loaded, select Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol as the Network connection method and either accept the default polcy name of NAP DHCP, or enter a new name for the policy:
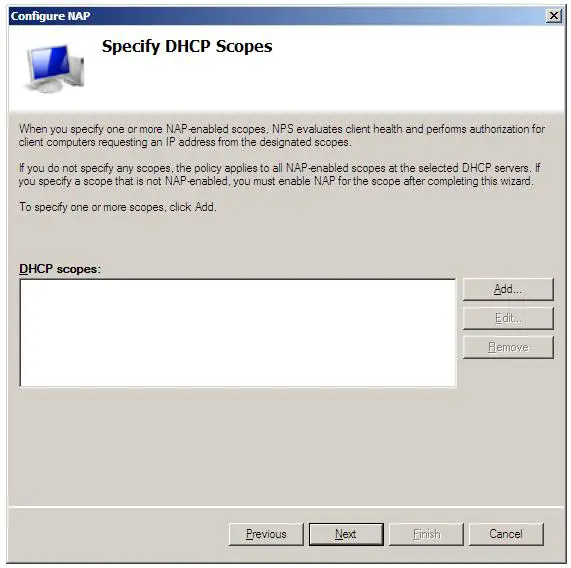
With these settings configured, click Next to display the NAP Enforcement Servers screen. If the DHCP Server is running on the local computer this screen can be skipped. On the other hand, if the remote DHCP servers are involved they must all have the Network Policy Server role installed and be added here. Click the Add... button and enter the name and IP address of the remote DHCP Server and either manually enter or generate a shared secret, which will need to be entered into the NAP DHCP policy of any remote DHCP servers added in this step of the process. Click Next to proceed to the DHCP Scopes screen:
If network client health is to be enforced for all IP addresses allocated by the DHCP server then no scopes need to be defined here. If, on the other hand, NAP enforcement is only required for certain IP address ranges, define the scopes here.
On the next screen enter specific machines and and users which are to be granted or denied access. the NAP Remediation Server settings page allows the addresses of Remediation Servers to be specified, where clients may obtain the necessary updates to reach NAP compliance. It is also possible to specify a web page URL which displays information to the user about how to bring their computers into compliance with the defined policy. When the appropriate information has been entered, click Finish to complete this phase of the configuration.
Configuring DHCP Server NAP Settings
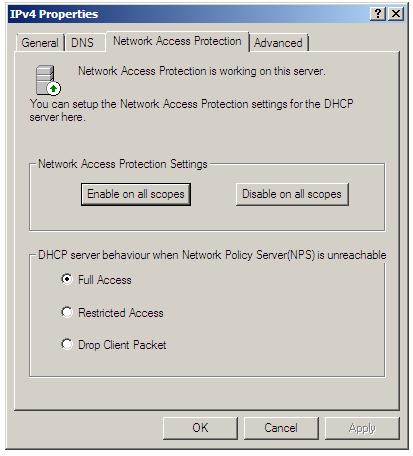
The NAP settings associated with a DHCP sever can be configured either on a server-wide (global) or per-scope basis. To configure global settings for a DHCP server, open the DHCP console (Start -> All Programs -> Administration Tools -> DHCP) and unfold the tree in the left panel for the required DHCP server. Right click on IPv4, select Properties and select the Network Access Protection tab as illustrated in the following figure:
Within this screen, Network Access Protection settings on all scopes can be enabled or disabled using the two buttons.