Difference between revisions of "Managing and Monitoring Fedora based Xen Guest Systems"
(New page: In the previous chapter (Installing and Configuring Fedora Xen Virtualization) we covered the steps necessary to configure the Fedora operating system to act as a Xen host system and c...) |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 14:15, 29 August 2007
In the previous chapter (Installing and Configuring Fedora Xen Virtualization) we covered the steps necessary to configure the Fedora operating system to act as a Xen host system and created, installed and ran a Xen guest system.
In this chapter we will explore the use of the virt-manager tool to manager the Xen guest operating systems.
Starting and Stopping Xen Guest Systems
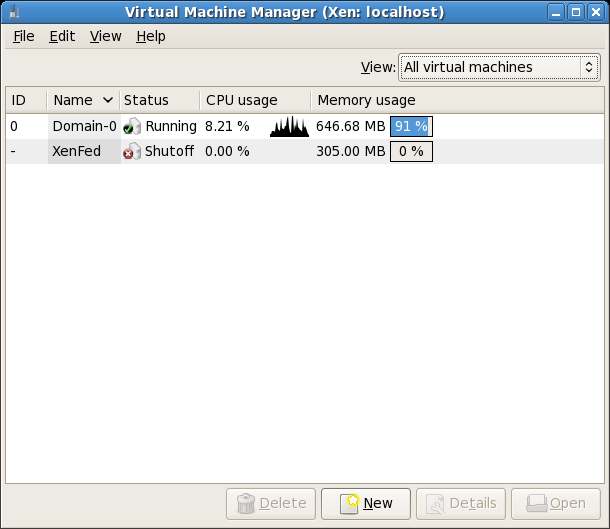
When a Xen guest operating has been configured it will appear in the list of systems when the virt-manager is loaded. The virt-manager tool is launched either by selecting the Applications->System Tools->Virtual Machine Manager or from the command-line by running /usr/sbin/virt-manager.
The following screenshot shows the virt-manager tool running on a Fedora system. It lists two systems - Domain 0 which is the host system, and a guest system named XenFed which is currently shut down: